After the invasion of Canaan under the leadership of Joshua, Ancient Israel extended 150 miles / 240 km from north to south, ‘from Dan to Beersheba’ (see 2 Samuel 24:2 and Map 34).
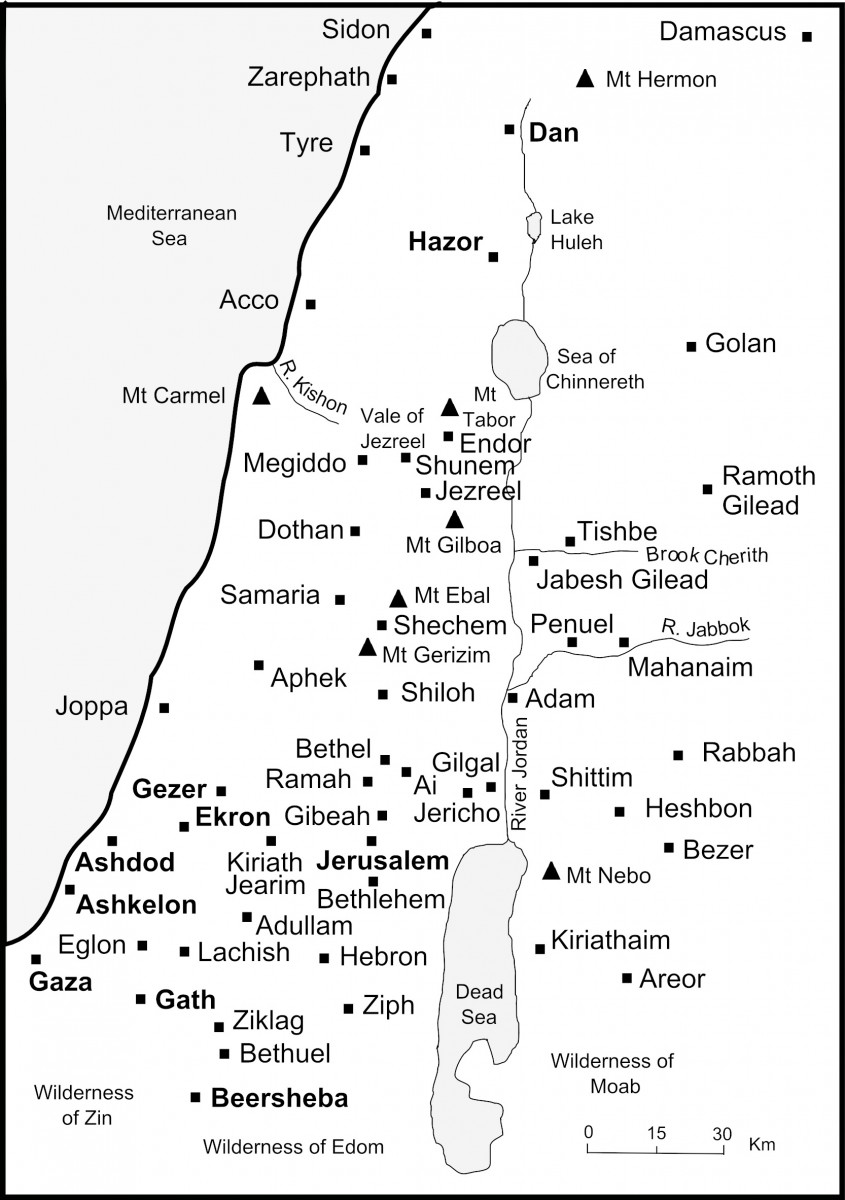
Map 34 Ancient Israel in the Old Testament
As the boundaries of Canaan set out by Joshua (see Numbers 34:1-12) and the boundaries of the Twelve Tribes of Israel (see Joshua 14:1-19:51) are broadly similar, it is often assumed that Israel controlled the whole of Canaan after the conquest in c.1406BC. This is, however, a gross simplification as much of the ‘promised land’ of Canaan remained unconquered for hundreds of years. Jerusalem, Hazor and Gezer, for example, remained independent Canaanite city-states for many years. For much of the following four hundred year period of the ‘Judges’, Israel was under the control of the Philistines, while the Philistine cities of Ashdod, Ekron, Ashkelon, Gaza and Gath were only eventually conquered by King David in c.1000BC (see 2 Samuel 5:17-25 & 8:1 and Map 34).
Ancient Israel was at its greatest extent under the rule of King David and his son Solomon, when the Kingdom of Israel and its vassal states stretched from the borders of Egypt to the banks of the River Euphrates (see 2 Samuel 8:2-14 & 1 Kings 4:20-21). Solomon took the wise political decision of allying with the neighbouring super-power Egypt. This meant that Israel was able to deploy the latest military technology - the iron chariot. With his network of strategically placed 'chariot cities', Solomon was able to extend his kingdom across the lowland plains beyond the Judaean uplands.
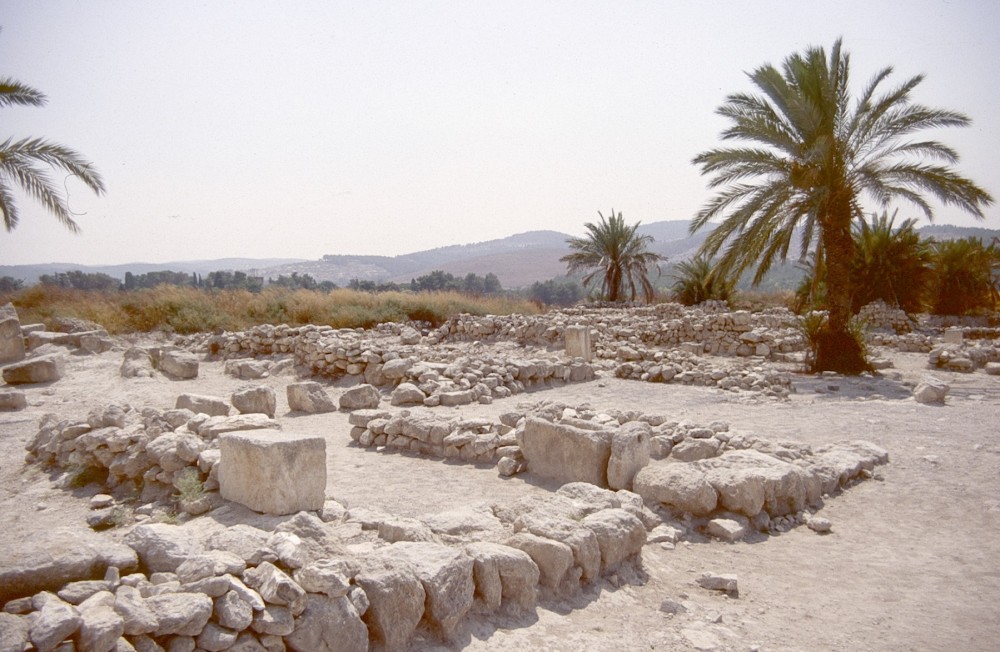

Stables at Megiddo housed the horses for King Solomon's war chariots
But this 'mega-Israel' lasted for only two generations - about 50 years. After this brief ‘glorious age’ during the ‘United Monarchy’, the country split in two. Repeated power struggles and civil wars during the ‘Divided Monarchy’ period ensured that both the remnant kingdoms of Israel and Judah were ultimately conquered by their neighbours – the northern kingdom of Israel by Assyria in 722BC, and the southern kingdom of Judah by Babylon in 587BC.
